I think sometimes, in the field of search marketing we try to make the concept of ranking more difficult than really it is. True - there are many ways to build a link, an endless number of keywords, thousands of exclusive sources to drive traffic all along with analytics, usability, design, conversion testing, etc. but, when it comes to the very precise question of how to rank well for a particular keyword in standard results at the engines, you're talking about a few big key components.
#1 - Keyword Use & Content Relevance
As I don't believe in keyword density, no doubt that using your keywords intelligently to create a page that are relevant to the query and the searcher intent is critical to ranking well. You can use the primary keyword phrase as follows:
.In the title tag once or possibly twice if it makes sense.
.one time in H1 header tag of the page
.At least 3X in the body copy on the page
.once in bold
.once in the alt tag of an image
.Once in the URL
.once in the meta description tag
.not in link anchor text on the page itself.
For who've done nonsense words testing to see engines respond, you know you can certainly get extra value out of going wild and filling the keywords all over the page, but we've also seen that once you reach this level of saturation you're getting about 95% of the value you can get.
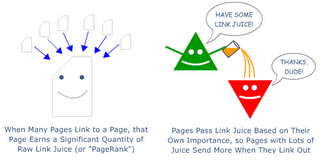
Some call this PageRank or link weight - it refers to raw quantity of global link popularity to the page. You can raise this with internal links and external links. A page with an exceptional amount of global link power can still rank remarkably well in Google & Yahoo!
Link juice operate on the fundamental principle used in the early PageRank formula - pages on the web have some inherent level of significance and that the link structure of the web can help to point out pages with greater and lesser value. Those pages linked to by many thousands of pages are very important and, when they link to other pages, those pages also have great importance.
Moving this theory to your own pages, you can observe how raw link juices have a large impact on the search engines score their rankings. Growing global link popularity needs both link building and intelligent internal link structure.
#3 - Anchor Text Weight
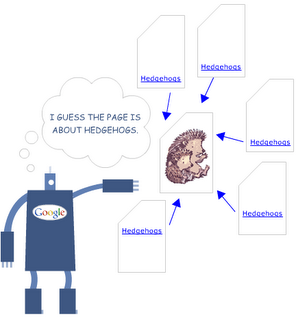
As search engines evolved in the early 2000's, they selected up on the usage of anchor text .The anchor text of links is a critical part of the ranking equation, and seen in great quantity, it could overshadow many other ranking factors - you could see many web pages weaker in all the other three factors I explain here ranking primarily because they've earned many thousands of links with the exact anchor text of the phrase they're targeting.
Note that anchor text come from both internal and external links, trying to optimize, think about how you're linking to from your own pages - using generic links or image links.
#4 - Domain Authority
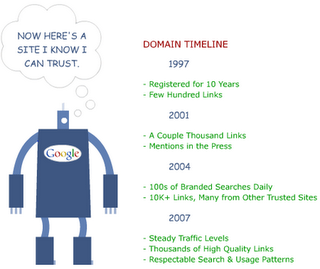
This is the most complex factors I described in this post. Basically, it refers to a variety of signals concerning a site that the search engines use to decide legitimacy. Does the field have a history in the engine? Do many people search for and use the domain? Does domain have high quality links pointing to it from other trustworthy sources?
To influence this positively, you need to do is operate your site in a way consistent with the engines' guidelines. If you desire to earn a lot of trust early in a domain's life, get many sites that the engines already trust to link to you.

posted by Skarmund
@ 7:02 PM
permanent link | |
![]()


Post a Comment