Software Project Management
Software project management research paper – web design and development plan
PROJECT SELECTION MODEL TO SELECT PROJECTS FOR SOFTWARE PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Prepared by Shipra Pandya and Khusboo Trivedi
ABSTRACT:
One of the most important tasks of software project management is the selection of prospective projects for development. Many organizations have developed a variety of sophisticated methods for screening and selection of projects in order to ensure that the firm does not have to face any pitfalls during the later stages of development. As part of the selection process, most of the firms adopt their own methods, based on their available data, technical criteria and organization’s policies.
All organizations select the projects they decide to pursue from among numerous options. Firms are literally bombarded with opportunities, but of course, no organization enjoys infinite resources to be able to pursue every opportunity that presents itself. Choices must be made, and to best ensure that they select the most viable projects, many managers develop priority systems—guidelines for balancing the opportunities and costs entailed by each alternative.
What criteria determine which projects should be supported? Obviously, this is no simple decision. The consequences of poor decisions can be enormously expensive. Recent research suggests that in the realm of information technology (IT), companies squander over $30 billion a year on projects that are created but never used by their intended clients.
All these call for an effective yet reliable process that highlights the various effective criteria to select a project that ensures development of successful products/software. Despite the availability of various existing models, there arises a need to address the “project selection” issue in a more detailed manner, which will cover all major and unseen criteria based on the size of the firms. The Project selection model proposed in this study will address this issue in a unique way, where; based on the size of the organization, the firm can check the required criteria that are necessary to select a project.
Index Terms: Software project management, Software project selection criteria, and project selection model.
INTRODUCTION:
Software project management is the process of effectively selecting projects and developing them which will be successful for the organization. Project selection plays a very important role in software project management, as it decides the success or failure of the project. Even though there are many other factors that play a vital role in the success or failure of the project, selection is the first phase that comes to the list.
Deciding whether or not to go ahead with a project is really a case of comparing a proposed project with a number of alternatives and deciding whether to proceed with it or not. When the project selection is made, a lot of criteria’s are taken into consideration before the organization decides to proceed. Selection of a project among a number of viable options will form the basis for every other activity that is undertaken following in the project. Many organizations have their own company policies that will decide whether or not to choose a project. Some organizations choose the strategic assessment method to choose a project, while other organizations follow the old traditional method of feasibility study that will check the advantages and disadvantages of undertaking a given project.
Feasibility study comes handy when small decisions are to be taken after choosing the project to be done. An example of feasibility study will be checking whether a particular feature incorporated in the software will be a good option or not. Feasibility study works well when small parts of the project are considered. There are many projects which are failing because of wrong selections made.
The traditional model for software project management known as the “step-wise- project planning model” emphasizes more on the development stages of the project. It assigns the phase “select project” to step 0, which indicates that the project selection stage is outside the main project planning process. But with the live examples that are seen in the real world, it is mandatory to give utmost importance to the project selection phase, where the organization decides whether or not to select a project. An independent process that will help organizations to select a project is the need of the day.
Projects are not initiated in thin air; some process needs to be there to decide which one to start with. It is not that a project is to be completely rejected if it doesn’t match the prescribed criteria. The right category that the project needs might be varying from one organization to another. It is just that project selection should be done carefully so that the organization does not suffer problems in the development phases.
The aim of this research paper is to propose a process model that will enable easy and efficient selection of software projects. The research paper will also project a comparative view of the traditional project selection criteria and the criteria put forth by the project selection model. The project selection model will categorize the types of organizations and based on the type of organization, the model will determine a set of criteria that will enable effective selection of projects.
The criteria determined by the project selection model will be subject to the type of organization. It is clearly understood that economic assessment of the project is done by every organization that does the project selection. The basis of classifying the type of organization in the project selection model will be based on the economic status of the concern so that the project that they choose will fall under their economic criteria.
PROPOSED WORK:
Project selection is making a commitment for the future. Project selection is the process of evaluating individual projects or groups of projects, and then choosing to implement one of them so that the objectives of the parent organization will be achieved. The proper choice of investment projects is crucial to the long-run survival of every firm. Daily we witness the results of both good and bad investment choices. The execution of a project will tie up the company resources, and as an opportunity cost the selection of one project may preclude your company from pursuing another project.
We live in a world of finite resources and therefore cannot carry out all the projects we may want or need. Therefore a process is required to select and rank projects on the basis of beneficial change to your company. There are many different techniques that can be used in project selection. Traditional methods that are in practice determine only whether to select the project or not. But as the technology is growing and the numbers of software projects are increasing, it is completely mandatory to select the project based on certain criteria. There are both numeric and non-numeric models are used in order to select projects. As the name implies, numeric models use numbers as inputs but the criteria being measured may be either objective or subjective. Non- numeric models are older and simpler and do not use numbers as inputs.
Some of the numeric models include:
- Present & Future Value
- Benefit / Cost Ratio
- Payback period
- Internal Rate of Return
- Annual Value
- Variations of IRR
A large majority of all firms using project evaluation and selection models use profitability as the sole measure of acceptability and hence use the numeric models to decide whether or not to select a project or not. But the drawback with these numeric models is that it does not focus on technological and commercial risk. Another disadvantage with numeric models is that they focus on a single decision criterion. There is need for a process model that highlights multiple selection criteria.
Some of the non-numeric models include:
- Unweighted 0–1 Factor Model
- Unweighted Factor Scoring Model
- Weighted Factor Scoring Model
- Constrained Weighted Factor Scoring Model
Non-numeric models are widely used by firms that do not want to focus on the profitability alone or those firms that want to assess the project based on non-numeric inputs. These models have multiple selection criteria that vary widely in their complexity and information requirements.
Hence it is observed that even though there are many proposed models both numeric and non-numeric, there is a necessity of a simpler model that is easy to implement and which gives desired results based on the type of organization. It is observed that the projects chosen sometimes do not match the type of organization that chooses them. Thus the “project selection model” will determine criteria based on the type of organization, enabling lesser failure of projects that occur due to wrong selection.
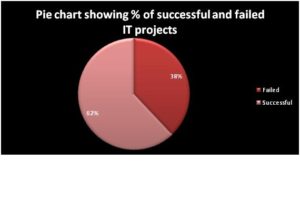
From a study, it is observed that 38% of projects fail in IT and only 62% work as planned. When the factors that are responsible for the failure of projects are considered, one among them is “wrong project selection”. If the wrong project selection criteria are taken care of, then there are chances that 38% can be brought down and the number of successful projects can be increased. The below mentioned chart determines the project success and failure percentage.
Keeping the current scenario in mind, the project selection model categorizes the organization that take up software projects into 3 categories. The classification is based on the economic criteria or the yearly turnover of the company in monetary terms. The 3 categories of the project selection model are E1, E2, and E3. The firms with highest turnover fall under the category E1, firms with lesser than that fall under category E2 and the firms with the least turnover mentioned fall under the category E3.
FIRM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON PROJECT SELECTION MODEL
It is observed that any IT company that takes up projects will have a turnover of 50k and more in Indian currency. Thus the least turn over category starts with the basic turnover and scales up to 6 Cr and more. It is clearly known that top IT companies have their turnover in millions and billions, those companies may also fall under the E1 category of the project selection model. The basic idea of categorizing the firms based on their economic value is to determine the criteria that will best suit the needs and type of the firm. These criteria will help determine the factors that are to be considered while making a project selection. These project selection criteria can be applied to the list of projects at hand and the project that best suits the company can be taken up.
The following criteria are to be considered when selecting a project.
| S.no | Criteria | Measurement scale |
| 1. | Performance of the project | High medium low |
| 2. | Technical literacy | 5 4 3 2 1 |
| 3. | Payback period | Number of years |
| 4. | Cost of development | High medium low |
| 5. | Profit from the project | High medium low |
| 6. | Time to market | High medium low |
| 7. | Development risk | High medium low |
| 8. | Project complexity | High medium low |
| 9. | Project flexibility | High medium low |
| 10. | Government safety standard | Yes no |
These are the ten criteria that are suggested by the project selection model that will be applied to each of the category of classification made by the project selection model. It is observed that these are the basic criteria that are needed for any project selection. These criteria together when applied to a project helps determine the selection of the project. Projects that are selected based on the criteria value suggested in the project selection model are less prone to failure and more efficient. The contexts in which these criteria are evaluated are:
- Performance of the project:
Performance of the project is calculated by comparing the proposed project with the other projects that are available for selection. The performance can be determined either by the cost or the purpose the project serves. The performance is rated in terms of high, medium or low. Projects with low performance are discarded from the list.
- Technical Literacy:
Technical literacy determines the technical skills that are required for the project to be developed and implemented. The technical skills of an employee may be in terms of number of years of experience. Hence the rating scale is from 5 to 1, with the highest technical literacy being 5 and lowest being 1.
- Payback period:
Payback period is the numeric model for evaluating the project. It is determined by the time taken to gain a financial return equal to the original investment. The time period is usually expressed in years and months. Hence the approximate payback period for E1, E2, and E3 is determined in number of years.
- Cost of development:
The cost of development criteria indicates the reasonable cost estimate for developing the project. The costs of all the proposed projects are calculated and rated on a scale high medium and low. The projects that fall under the high category are considered last, as those projects might have a return on investment.
- Estimated Profit from the project:
The profit that will be derived from the project is estimated by subtracting the expect income from expected expenditure that will be incurred. Profits of all the projects are calculated and rated on a scale of high medium and low. Projects falling under the category low are discarded.
- Time to market:
Time to market criteria is for projects that are generic. If the time taken to promote the project is more than the development then such projects have no value. Thus the time taken to market can be calculated in months or years (take common parameter for all projects) and rated on high, medium and low scale.
- Development risk:
The development risk of a project is the risk that the company faces during the development phases. It can be requirements risk, lack of resources, lack of personnel, change in requirements etc. all the risks pertaining to development are identified and ranked on the high, medium and low scale. Projects with high development risk are not considered.
- Project complexity:
The complexity of the project can be determined by the complexity factors such as LOC (lines of code), FP (function points), and man hours required for the development of the project. These complexity factors are calculated on a high medium and low scale.
- Project flexibility:
Project flexibility is a very important criterion when selecting projects. Flexibility refers to the capability of the project to adapt to changing environment. Portability and interoperability factors are checked to determine the project flexibility. The project flexibility is also ranked on a high, medium and low scale.
- Government safety standard:
The government safety standard is the last criteria proposed by the project selection model. It checks to determine if the project developed is abiding to the legal rules and regulations and is in the government safety standard list. This criterion is rated on a yes/no scale.
The desired values for any category of organization are:
| Performance of the project | High |
| Technical literacy | 5 |
| Payback period | 1year |
| Cost of development | Low |
| Profit from the project | High |
| Time to market | low |
| Development risk | Medium |
| Project complexity | Low |
| Project flexibility | High |
| Government safety standard | yes |
But as it is observed no project fulfills all the criteria in the desired rating scale, the project selection model applies these 10 criteria to the 3 categories classified by the project selection model. The desired values that the criteria should possess are specified in the project selection model below.

It is observed that the category E1 organizations can select projects that have technical literacy 3, 2 as the organization s capable of hiring training teams. But the E3 category cannot select projects with such medium technical literacy as the turnover will be low and the organizations cannot afford to spend on training and development; as the cost incurred might affect the profit of the concern.
Thus the project selection model aims to simplify the project selection mechanism in a way that the projects selected using this process does not end up in failure.
PROJECT STUDY
Case: A company has selected an alpha project based on a numeric model namely Payback Period. As the name suggests, the selection of a project among varied choices will be made based on the period of time required to recoup the funds expended in a given project. Projects with shorter payback periods will be preferred over longer payback period projects. The company has selected the alpha project after evaluating it with other alternative projects depending upon the criteria under Payback period.
The same alpha project is undertaken and selection model is applied to derive at a conclusion of whether a project selected by using other numeric and non-numeric models can be selected when the selection model is used for evaluation. The criteria in the selection model are applied to the alpha project to determine the following values:
| Performance of the project | Medium |
| Technical literacy | 3 |
| Payback period | 3 year |
| Cost of development | Medium |
| Profit from the project | High |
| Time to market | High |
| Development risk | Medium |
| Project complexity | Low |
| Project flexibility | High |
| Government safety standard | Yes |
For a project to be selected, the below mentioned requirements are to be met:
- The technical literacy rate should be greater than or equal to 3.
- Payback period should be as low as possible
- Cost of development can vary depending upon the size and complexity of the project
- Time taken to market the proposed project should be less than the overall development time. Hence, preferably it should be low.
 It is observed that the alpha project is not feasible when the selection is made using the proposed selection model since it does not satisfy the requirements mentioned in each category. Although the cost of developing an alpha project is medium, it’s payback period according to the selection model will be 3 years. A company would be interested in such projects whose cost of development and payback period will be as low as possible. Other criterion that does not meet the stated values is time to market which is high signifying that it will require additional time to market the project above the time taken to develop the project. The value of performance of the project is also medium, which along with other non-satisfactory criteria, is the most important reason of not selecting the alpha project.
It is observed that the alpha project is not feasible when the selection is made using the proposed selection model since it does not satisfy the requirements mentioned in each category. Although the cost of developing an alpha project is medium, it’s payback period according to the selection model will be 3 years. A company would be interested in such projects whose cost of development and payback period will be as low as possible. Other criterion that does not meet the stated values is time to market which is high signifying that it will require additional time to market the project above the time taken to develop the project. The value of performance of the project is also medium, which along with other non-satisfactory criteria, is the most important reason of not selecting the alpha project.
Henceforth, the alpha project which was selected when Payback Period numeric model was adopted cannot be selected when selection model is applied to it. The type of model used for selecting a project greatly depends upon the nature, objectives and size of the company. It is not always necessary that a project that is found appropriate when using a particular model will be favorable when a different model is used.
CONCLUSION
Project selection is a very vital stage that any company goes through. Selecting the right project is a very mandatory decision that any company takes. If any wrong project is selected, the development and future execution of the project is bound to suffer. According to various researchers and practitioners, project selection is a risk in itself, whose consequences are uncertain. There are many project selection models that exist, which enable project selection easier. But the project selection model proposed in this research paper is a combination of both numerical and non numerical project selection models that determines criteria based on the turnover categories of the company.
The turnover of any company determines which category the company belongs to, and determines which criteria can be adjusted according to the category of the company which will determine whether a prospective project will be selected or not. Thus it is recommended that the project selection model be used to select prospective projects in any company which will ensure no wrong projects are selected, and selected projects turn out to be successful.
REFERENCES
- Software project management, third edition, Bob Hughes and Mike Cotterll
Prepared by Shipra Pandya and Khushboo Trivedi
Search
Categories
Recent Posts
- <strong>Create SEO-Optimised Articles Using ChatGPT In 7 Simple Steps</strong>
- <strong>14 Tips & Techniques for SEO Article Writing </strong>
- <strong>14 Tips & Techniques for SEO Article Writing </strong>
- <strong>10 Best SEO Audit Tools</strong>
- <strong>How to Do an SEO Competitor Analysis (Step-By-Step)</strong>